- 11 Aug, 2020
- /
- Category:
- Advanced Wound Care
Hydrogels -- Beyond Debridement Applications
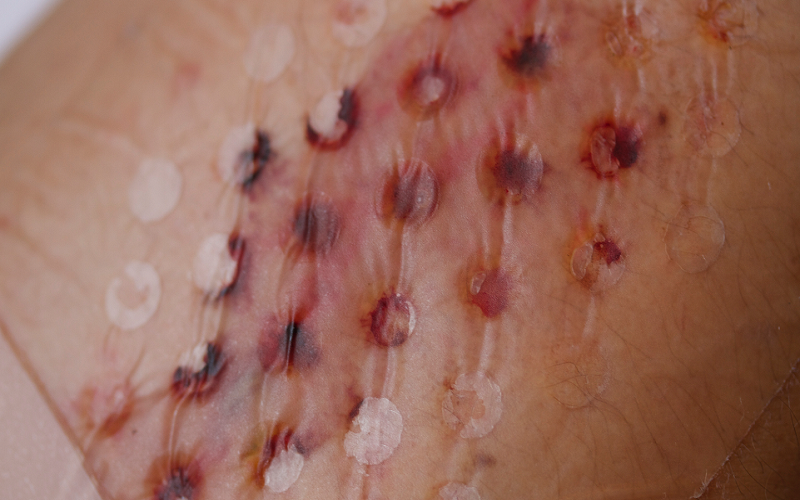
Hydrogels have long been a staple for advanced wound and burn care to facilitate debridement -- the removal of damaged tissue or foreign objects from a wound. Hydrogels can absorb and retain wound exudates, promoting fibroblast proliferation and keratinocyte migration – which is pivotal for successful epithelialization and healing.[1] As part of wound dressings, hydrogels have been demonstrated to support skin healing and protect afflicted areas from infection. The high-water content of hydrogels – which is comparable to that of human tissue – gives hydrogels the flexibility and elasticity to adapt to wounds located on different sites across the body. Hydrogels can also support moist wound healing, which may potentially aid in faster recovery times with reduced scarring.
Due to the biocompatibility, breathability, absorbency and cushioning properties, hydrogels are actually one of the most versatile types of adhesives and used in a broad range of applications.
Because of their translucency properties, hydrogels allow medical care providers to monitor the healing process of the surgical sites, acute and chronic wounds without incurring in frequent dressing removal, which help to minimize further trauma to the area.
A type of hydrogels called tough gels are a good option as scaffold material for tissue engineering applications because their structures are similar to the extracellular matrix of human tissue. These hydrogels materials are biocompatible and can often be processed under relatively mild conditions whilst being delivered in a minimally invasive manner. [2]
Beyond advanced wound and burn care and tissue engineering, hydrogels are being explored for controlled drug delivery applications for predefined periods of time. Hydrogels have a very porous structure, making them highly permeable to different kinds of drugs and allowing drugs to be loaded and, in proper conditions, released.[3]
Hydrogels also have significant potential for consumer applications. From being used to cushion blisters and protect minor abrasions at home, to incorporation in cosmetic skin care products. For example, hydrogels may be infused with active and skin friendly compounds, such as aloe vera and botanicals, to provide a highly moisturizing and soothing gel for under eye pads and face masks.
Scapa Healthcare is able to provide a high degree of flexibility in the formulation of hydrogel-based products. Unlike typical hydrogels, which consist of 90% water, we use proprietary processes to vary and control our water rates – ranging from around 30%-70%, allowing greater manipulation over the products’ properties such as adhesion and cooling. Thus, we are able to offer customized hydrogel solutions that best meet end-users’ needs.
_____
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315442/
[2] K.Y. Lee, D.J. Mooney, Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering, Chem. Rev. 2001; 101(7): 1869-1877, DOI: 10.1021/cr000108x
[3] M. Bahram, N. Nurallahzadeh, N. Mohseni, pH-sensitive Hydrogel for Coacervative Cloud Point Extraction and Spectrophotometric Determination of Cu(II): Optimization by Central Composite Design, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2015; 12(10): 1781-1787, DOI: 10.1007/s13738-015-0653-5
